In fact, we talked about surface treatment. We all know that plating actually plays two roles: one is to decorate the appearance, and the other is to protect the substrate from corrosion. To put it plainly that this article Shanghai dumping technology is to explore why electroplating products do salt spray corrosion test? The quality of plating quality appreciation is indispensable to our standard salt spray test specification.
1. What is salt spray corrosion?
Salt spray corrosion is a common and most damaging atmospheric corrosion. Corrosion is the destruction or deterioration of a material or its properties caused by the action of the environment. Most of the corrosion occurs in the common atmosphere. Why? The atmosphere contains oxygen, humidity, temperature changes, and contaminants such as corrosion and corrosion factors. Today we discuss the corrosion of salt fog: the most important component of salt spray corrosion is the chloride salt in the ocean, which is mainly from the saline and alkaline regions of the ocean and the interior.
The corrosion of the surface of the metal material by the salt spray is caused by the electrochemical reaction between the contained chloride ions penetrating the metal surface oxide layer and the protective layer and the internal metal. At the same time, the chloride ion contains a certain amount of hydration energy, which is easily adsorbed on the pores and cracks on the metal surface to displace and replace the oxygen in the chloride layer, transforming the insoluble oxide into soluble chloride, and making the passive state surface become lively. surface. Caused a very bad adverse reaction to the product.
2. The correlation between salt spray test and actuality In simple terms, the salt spray test is an environmental test that uses the salt spray test equipment to artificially simulate the salt spray environmental conditions to conduct a rigorous test to evaluate the corrosion resistance of a product or metal material.
The salt spray test is basically divided into two categories, a type of natural environmental exposure test, and another type of artificial accelerated salt spray environmental test. The latter is the use of a test equipment with a certain volume of space - salt spray corrosion test box, in its volumetric space with artificial methods, resulting in a salt spray environment to assess the product's resistance to salt spray corrosion quality.
The latter is more demanding than the former (natural environment). The amount of artificially controlled salt spray can be said to be several times or even several times that of the normal natural salt spray. Such a large amount of salt spray has a very fast corrosion rate. It cannot be said that the corrosion rate can be greatly improved, thereby shortening the test time, and has a significant advantage compared with the natural exposure environment. It may take up to one year or even longer in a natural exposure environment. In artificially simulated salt spray environments, it may take only 24 hours to achieve similar results.
3. Artificial simulated salt spray tests include three types: neutral salt spray test (NSS test), acetate spray test (ASS test), copper salt accelerated acetate spray test (CASS test)
1) Neutral salt spray test (NSS test) is the earliest present application of an accelerated corrosion test method. It uses a 5% aqueous chloride solution and the pH of the solution is adjusted to a neutral range (6 to 7) as a spray solution. The test temperature is taken at 35°C, and the deposition rate of salt spray is required to be between 1 and 2ml/80cm2.h.
2) Acetate spray test (ASS test) was developed based on the neutral salt spray test. It is to add some glacial acetic acid to the 5% solution, so that the PH value of the solution is reduced to about 3, the solution becomes acidic, and the final salt fog is also changed from neutral salt fog to acidic. Its corrosion rate is about three times faster than the NSS test.
3) Accelerated Acetate Salt Spray Test (CASS test) is a rapid salt spray corrosion test recently developed abroad. The test temperature is 50 °C. A small amount of copper salt, cupric chloride, is added to the salt solution to strongly induce corrosion. Its corrosion rate is about 8 times that of the NSS test.
4. Judgment of salt spray test standard results A. Standards are unified provisions for repetitive things and outlines. The salt spray test standard is a specific and specific requirement for salt spray test conditions, such as temperature, humidity, solution concentration, and pH, and it also provides technical requirements for the performance of the salt spray test chamber. The salt spray test standard for the same product should be selected based on the characteristics of the salt spray test and the metal corrosion rate and sensitivity to salt spray.
B. The purpose of the salt spray test is to evaluate the salt spray corrosion resistance of a product or metal material. The determination of the salt spray test result is the judgement of the product quality. The determination result is correct and reasonable. It is a correct measure of the product or metal resistance. The key to salt spray corrosion quality.
C. Judgment methods for salt spray test results include: rating determination method, weighing determination method, corrosion material appearance determination method, and corrosion data statistical analysis method.
1) The rating method is to divide the percentage of the ratio of the erosion area to the total area into several levels according to a certain method. A certain level is used as a criterion for the evaluation. It is suitable for flat plate samples for evaluation; 2) The weighing method is adopted. The weight of the sample before and after the corrosion test is weighed, and the corrosion-damaged weight is calculated to evaluate the corrosion resistance of the sample. It is particularly suitable for assessing the corrosion resistance of a certain metal; It is a qualitative judgment method. It judges the sample after the salt spray corrosion test, whether the product is corroded. This method is mostly used in the general product standards. The corrosion data statistical analysis method provides the design corrosion test and analyzes the corrosion data. The method of determining the confidence level of the corrosion data is mainly used to analyze and count the corrosion situation, instead of specifically determining the quality of a specific product.
Feiyiya Inclined Plate Clarifiers Use Gravity & Innovative Engineering
A gravity clarifier is the most economical method of removing solids from liquids, using natural gravity as the source of energy and it is free. A clarifier simply provides a non-turbulent zone where heavier than liquid solids, suspended by turbulence, are given sufficient time to settle to a quiescent surface. The HEI inclined plate clarifiers are compact units with multiple layers of settling area utilizing less than 25% of the floor space required by conventional clarifiers.
Principle of Clarifiers
A particle carried forward by the velocity of the liquid flow must settle at a rate that allows it to reach the bottom before passing through the clarifer. Thus, particles beginning at a point [a" must traverse some route lying between ab and ab` in order to avoid being carried over the outlet.
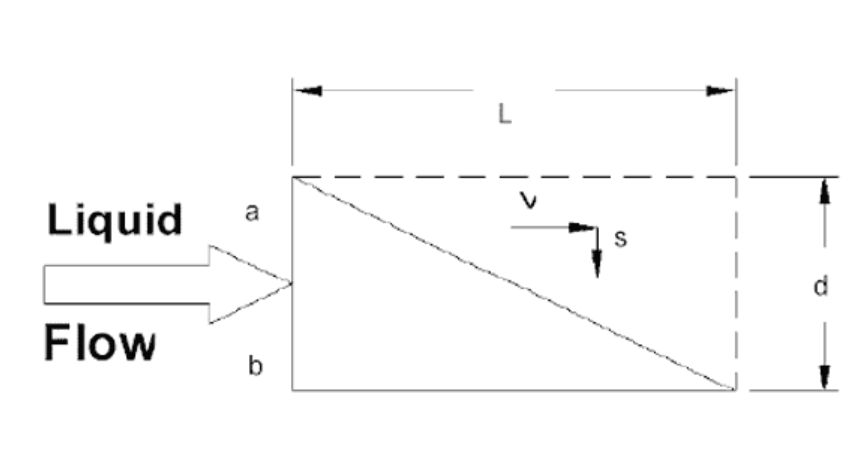
If V is the horizontal velocity of the liquid, S the solids particle vertical settling velocity, L the length of the settling device, and D its depth, then particles entering at point A will settle to the bottom of the device only if V does not exceed: S(L/D)Since Vmax / S = L / D then, Vmax = S (L / D)
Therefore, the velocity at which a horizontal clarifying device may be operated successfully is directly proportional to its length and inversely proportional to its depth.
This analysis applies to multiple horizontal plate units also. The spacing between plates is usually a few inches as opposed to a depth of several feet in a horizontal tank; therefore, [settling-out" times are dramatically reduced. The flow must be non-turbulent to prevent settled solids from being re-entrained within the moving liquid. Small plate spacing and a large surface area permits laminar flow at higher velocities than large horizontal tanks would allow.
Horizontal clarifying devices become self-flushing if they are inclined at an angle which exceeds the angle of repose of the settled solids. In such cases, flow enters the lower end of the device where settling particles move to the floor eventually sliding back out the entrance. Clear effluent leaves the top of the device.
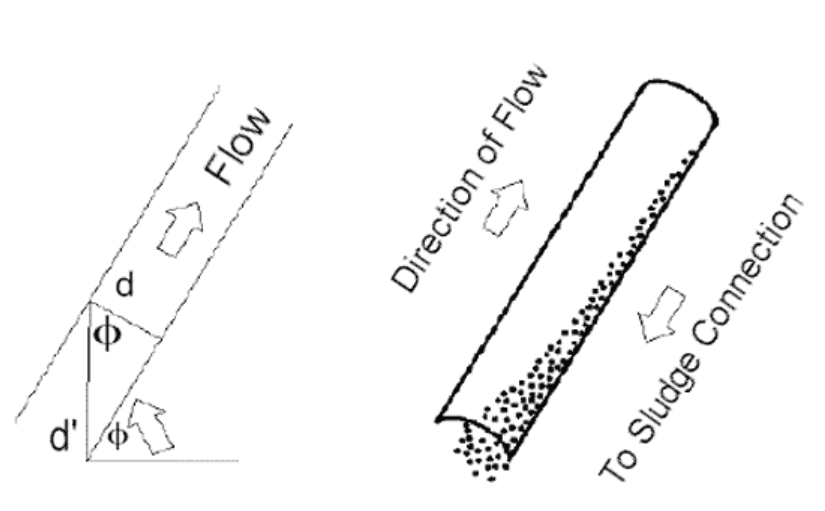 However, when the device is inclined, the furthest settling particles no longer fall through distance D but some longer distance D`. This new longer settling distance D` is related to D by the relation: D = D` cos Ø.
However, when the device is inclined, the furthest settling particles no longer fall through distance D but some longer distance D`. This new longer settling distance D` is related to D by the relation: D = D` cos Ø.
Theta [Ø" is the angle, the device is inclined to the horizontal plane. Thus settling distance is increased by the factor: 1/cos Ø In the case where Ø = 60º, 1/cos Ø = 2.
The maximum settling distance is twice the distance between the plates. It is apparent then that the lower the angle of inclination, the smaller the settling distance. However, the angle of inclination must exceed the angle of repose of the solids to be separated. The previous equation may be modified to express the cosine of an inclined plate clarifying system as:
Vmax = L / (D / cosØ) (s) = L·cosØ / D (s)
Inclined Plate Clarifiers
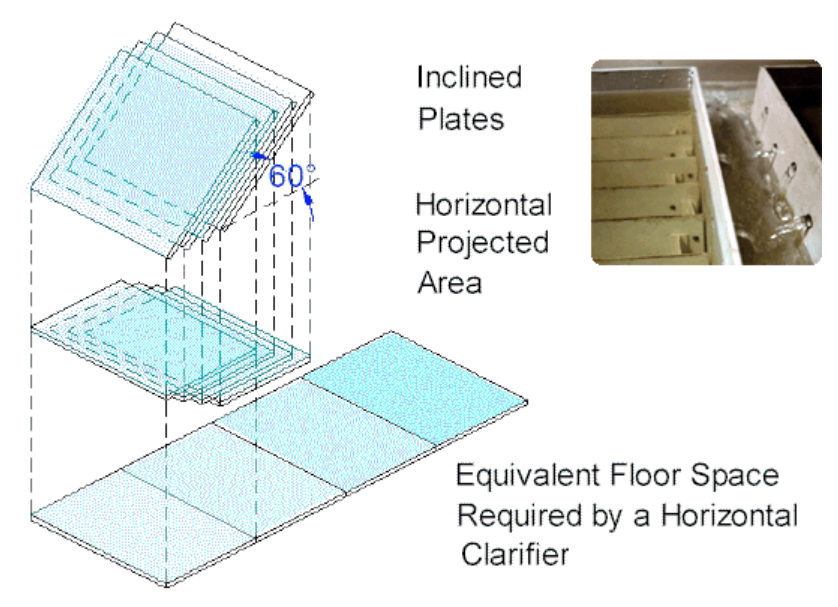
A reduction of the required floor space is acquired by diminishing the separation between the horizontal plates to a few inches and stacking the settling surfaces. Inclining the plates to provide self flushing, 45º for heavy particles and 60º for light particles, reduces the available horizontal projected area (effective settling area) by a factor equivalent to the cosine of the angle. The surface area diagram (below) graphically compares the floor space requirements of an HEI inclined plate clarifier with the equivalent horizontal projected settling area.
Settling Rate
The settling rate for a specific solids should be determined by standard laboratory tests. Light particles, such as metal hydroxides, usually require a design parameter of 0.25 – 0.50 gallons per minute per square foot of horizontal projected area. These low density solids require the inclined plates to be set at a 60º angle to induce the particles to slide down the plate. Heavier particles (such as sand that easily flow) will readily slide from plates set at a 45º angle.
Maximum flow rate of an inclined plate clarifier is based on the flow rate per unit of a horizontally projected surface area. Retention time in the clarifier is not a design criteria. However, attaining optimum performance requires the prudent design to recognize several additional, very important factors.
Inclined plate clarifier, Lanmei inclined plate clarifier, Inclined Tube Settler,High-Efficiency Inclined Tube
Wuxi Feiyiya Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.feiyya.com