The Truth Behind Compliant Composite Repairs: Matching Standards to Real-World Defects
Compliance with repair standards is crucial to ensuring the safety and longevity of process piping. For composite repair systems, being compliant with standards like ASME PCC-2 is required for assets operating at extreme pressures and temperatures. However, engineering repairs must go beyond technical calculations. It is possible to install an ineffective, yet technically compliant repair. Avoiding this situation is critical and possible with clear communication and proactive planning.
What is a Compliant Repair?
A composite repair system must be designed in accordance with industry standards and regulations. For pressure equipment and piping, the composite must conform to standards set in ASME PCC-2. Compliance with this standard ensures that all repairs are completed safely and efficiently, reducing the risk of failure and extending the equipment’s lifespan.Â
While a composite’s compliance with these standards is essential, meeting these standards goes beyond the design calculated on paper. In practice, the effectiveness of the composite repair depends more on being designed for the defect at hand as not all defects in the field are identical. This is where the disconnect between the design and actual repair can arise.Â
The Disconnect between the Design and the Actual Repair
A composite repair’s full functionality depends on the defect to be repaired, a proper design, and correct installation. In standard situations, the end user identifies damage, who contacts an installer. A composite manufacturer is then included in the design process for a quote and design data sheet, which details the layers needed for the repair. This requires the parties involved with the repair (the end user, installer, and designer) to not only understand the defect but also have clear communication on the full nature of the defect in the field.Â
Defect Transformation: From Circular to Circumferential Slot
For example, take a pinhole defect. A pinhole defect is classified as a circular or near-circular hole defect under ASME PCC-2 Type B designs. Type B designs are for leaking components or components that have less than 0.04†wall thickness at any point while the repair is in service. A composite cannot be installed over an active leak, and typically, the line cannot be shut down. Even if the component has been stop-gapped, it is still a Type B repair.
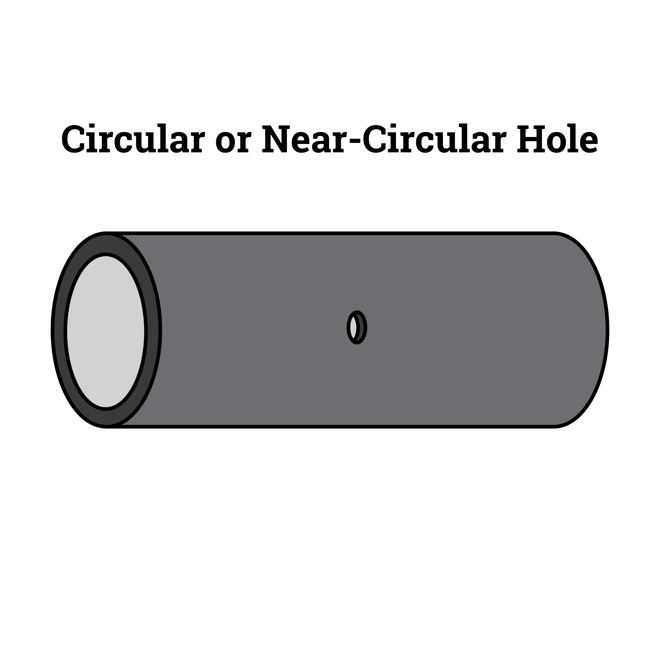
If you seal that leak with a band clamp around the pipe, that changes the defect’s size and geometry, leading it to transition to a circumferential slot defect which requires a different design calculation. For a design pressure of 250 psi, the circular hole defect equation results in 4 layers, while the circumferential slot equation results in 12 layers. By going with the circular hole defect repair, the composite will be too thin and could potentially fail.

To learn more about Type B designs under ASME PCC-2, read this article.Â
Impact of Mismatched Calculations
A mismatched calculation can result in a composite repair with fewer layers and potentially failing over time. Depending on the design, it may be recovered and recalculated, but this depends on how long the repair has been present and whether it has been protected, i.e., with a UV coating. If it hasn’t been protected, additional layers can be applied. If it has been, the repair needs to be completely redone.Â
Bridging the Gap
It's important to ensure all factors are taken into consideration when giving the information to the engineer. The answer to these two key questions should be given to the designer.
- What has happened, and what is the defect?
- What has been done to repair the defect already?
On the designer side, it’s important to ensure the right calculations are used. HJ3 references all calculations to match the defect, standards, and regulations.Â
While compliance with industry standards is critical in designing a composite repair system, it’s only half the battle. Field conditions and repairs often transform the defects, requiring different calculations in the design. Ensuring the right design is used for the right defect can prevent costly failures and future repairs. By maintaining clear lines of communication between all parties involved to ensure accurate designs are calculated, the composite repair will be compliant and fully effective.Â
If you’re interested in learning more or would like an engineering presentation for you and others, contact HJ3 for support.Â
â€
I. Introduction to ZHTE HYDRAULIC Excavator Excavator Hydraulic Pump
II. Product Introduction and Categories
III. Production Process

V. Enterprise Qualification
Our products
Hydraulic Excavator Pump,Hydraulic Pump Mini Excavator,Excavator Parts Hydraulic Pump,Main Hydraulic Pump
XINGTAI ZHONGWEI ZHUOTE HYDRAULIC TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.zwzhtehydraulic.com