A pH meter is an instrument used to determine the pH value of a solution. The pH meter works on the principle of the galvanic cell. The electromotive force between the two electrodes of the galvanic cell depends on the specific law of the energy, which is related to the self-property of the electrode and the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution. There is a correspondence between the electromotive force of the primary battery and the hydrogen ion concentration, and the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration is the pH value. pH meter is a common analytical instrument widely used in agriculture, environmental protection and industry. Soil pH is one of the important basic properties of soil. Factors such as the temperature of the solution to be tested and the ionic strength should be considered during the pH measurement. [1]

What is pH? pH is an abbreviation for the Latin word "Pondus hydrogenii" (Pondus = pressure, pressure hydrogenium = hydrogen), used to measure the activity of hydrogen ions in a substance. This activity is directly related to the acidity, neutrality and basicity of the aqueous solution. Water is chemically neutral, but not without ions, even if chemically pure water is also slightly dissociated: Strictly speaking, the hydrogen nucleus does not exist in a free state until it is hydrated with water molecules.
H 2 O+ H 2 O=H 3 O + + OHˉ, since the concentration of hydronium ion (H 3 O + ) is equivalent to the hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration, the above formula can be simplified into the following common forms:
H 2 O=H + + OHˉ
The positive hydrogen ion here is expressed in the chemical as "H + ion" or "hydrogen core". The hydrated hydrogen nucleus is represented as "hydrated hydrogen ion". Negative hydroxide ions are referred to as "hydroxide ions."
Using the law of mass action, an equilibrium constant can be found for the dissociation of pure water:
K=H 3 O + ×OH - ————H 2 O
Since only a small amount of water is dissociated, the mass molar concentration of water is actually a constant, and there is an equilibrium constant K to determine the ion product KW of water.
KW=K×H 2 O KW= H 3 O + ·OH-=10 -7 ·10 -7 =10 -14 mol/l (25°C)
That is to say, for one liter of pure water, there are 10 -7 moles of H 3 O + ions and 10 -7 moles of OH ˉ ions at 25 ° C.
In the neutral solution, the concentration of hydrogen ion H + and hydroxide ion OH 都是 is 10 -7 mol/l. Such as:
If there is an excess of hydrogen ion H + , the solution is acidic. The acid is a substance which can release the hydrogen ion H + in the aqueous solution. Similarly, if the OH ˉ ion is freed, the solution is alkaline. Therefore, giving the H + value is enough to indicate the characteristics of the solution, whether it is acidic or alkaline. In order to avoid the calculation of the negative concentration index of this molecular concentration, the biologist Soernsen suggested this inconvenience in 1909. The value is replaced by a logarithm and is defined as "pH". The mathematically defined pH is the common log negative value of the hydrogen ion concentration. That is, pH = -log [H + ].
Therefore, the pH is the negative of the base 10 logarithm of the ion concentration:
Changing the pH of 50 m 3 of water requires 500 L of bleach from pH 2 to pH 3. However, only 50 L of bleach is required from pH 6 to pH 7.
There are many methods for measuring the pH value, mainly chemical analysis method, test paper method, and potential method. Now we mainly introduce the pH value measured by the potentiometric method.
The electrode used in the potential analysis method is called a primary battery. A primary battery is a system whose function is to convert chemical reaction energy into electrical energy. The voltage of this battery is called the electromotive force (EMF). This electromotive force (EMF) consists of two half-cells, one of which is called the indicator electrode, its potential is related to the specific ion activity, such as H + ; the other half-cell is the reference half-cell, usually called the reference The specific electrode, which is generally connected to the measuring solution, and is connected to the measuring instrument.
For example, an electrode is made of a silver wire inserted in a salt solution containing silver ions. At the interface between the wire and the solution, ions are formed due to different activities of silver ions in the two phases of the metal and the salt solution. The charging process and form a certain potential difference. Lost electrons of silver ions into the solution. When no external current is applied for reverse charging, that is, there is no current, the process will eventually reach a balance. The voltage present in this equilibrium state is referred to as a half-cell potential or an electrode potential. Such an electrode (as described above) consisting of a metal and a solution containing the metal ion is referred to as a first type of electrode.
This potential is measured relative to a reference electrode whose potential is independent of the composition of the salt solution. Such a reference electrode having an independent potential is also referred to as a second electrode. For such electrodes, the metal wires are covered with a layer of a slightly soluble salt of such a metal (e.g., Ag/Agcl) and inserted into an electrolyte solution containing such metal salt anions. The half cell potential or the electrode potential at this time depends on the activity of such an anion.
The voltage between the two electrodes follows the Nernst formula:
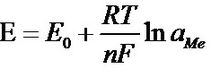 Nernst formula
Nernst formula
Where: E-potential
E0—the standard voltage of the electrode
R—gas constant (8.31439 joules/mole and °C)
T-Kelvin absolute temperature (example: 20 ° C equivalent to (273.15 + 20) 293.15 Kelvin)
F-Faraday constant (96493 library / equivalent)
N—the valence of the measured ion (silver=1, hydrogen=1)
Ln(aMe)—the logarithm of the ion activity aMe
The standard hydrogen electrode is the reference point for all potential measurements. The standard hydrogen electrode is a platinum wire which is electroplated (coated) with platinum chloride and filled with hydrogen gas (fixed pressure of 1013 hpa).
The electrode was immersed in a solution having a H 3 O + ion content of 1 mol/l at 25 ° C to form a half-cell potential or electrode potential referenced for all potential measurements in the electrochemical. The hydrogen electrode as a reference electrode is difficult to implement in practice, so a second type of electrode is used as a reference electrode. The most commonly used one is the silver/silver chloride electrode. The electrode reacts to changes in chloride ion concentration by dissolved AgCl.
The electrode potential of this reference electrode is made constant by a saturated kcl reservoir (eg 3 mol/l kcl). An electrolyte solution in the form of a liquid or gel is connected to the solution to be tested through a membrane.
The silver ion content in the film rinsing liquid can be measured by using the above electrode combination-silver electrode and Ag/AgCl reference electrode. It is also possible to replace the silver electrode with a platinum or gold electrode for the measurement of the oxidation-reduction potential. For example: the oxidation phase of a certain metal ion.
The most commonly used pH indicating electrode is a glass electrode. It is a glass that is blown into a bubble-like pH-sensitive glass film. The tube was filled with a 3 mol/l kcl buffer solution containing saturated AgCl at a pH of 7. The potential difference reflecting the pH on both sides of the glass film is controlled by an Ag/AgCl conduction system.
Such as the second electrode, derived. pH composite electrode and pH solid electrode,
This potential difference follows the Nernst formula:
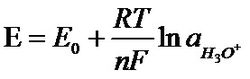 Nernst formula
Nernst formula
Substituting values ​​such as E 0 , R, T (298.15K or 25 ° C) into the above formula:
E=59.16mv/25°C per pH (in the formula, ln(H 3 O + ) has been converted to pH)
Where R and F are constants, n is the valence, and each ion has its fixed value. For hydrogen ions, n=1. The temperature "T" is used as a variable and plays a large role in the Nernst formula. As the temperature rises, the potential value will increase.
The increase in temperature per 1 °C will cause a potential change of 0.2 mv/per pH. The pH value indicates a pH change of 0.0033 per 1 °C.
This means that there is no need to compensate for temperature changes for measurements between 20 and 30 ° C and around 7 pH; for temperature applications > 30 ° C or < 20 ° C and pH > 8 or 6 Make compensation.
Industrial pH meter is a commonly used industrial instrument equipment, which is mainly used to accurately measure the pH value of liquid medium. And considerations for installation, cleaning, anti-jamming, etc.
According to the needs of production and life, people have scientifically researched and produced many types of acidity meters:
According to measurement accuracy
Can be divided into 0.2, 0.1, 0.01 or higher precision.
By instrument volume
It is divided into pen type (mini), portable, desktop and online continuous monitoring and measurement online.
According to the requirements of use
Pen-type (mini) and portable pH pH meters are generally used by inspectors for on-site inspection.
The accuracy level of the pH pH meter is selected according to the accuracy required by the user's measurement, and then various pH meters are selected according to the user's convenience.
â—† According to portability, it is divided into: portable pH meter, benchtop pH meter and pen type pH meter.
â—† According to the use, it is divided into: laboratory pH meter, industrial online pH meter, etc.
â—†According to the advanced degree, it is divided into economical pH meter, intelligent pH meter, precision pH meter or pointer type pH meter, digital display pH meter.
â—†Pen type pH meter, generally made into a single range, narrow measurement range, is a special and convenient instrument.
Portable and benchtop pH meters have a wide measurement range and are commonly used. The difference is that the portable DC power supply can be carried to the site. The laboratory pH meter has a wide measuring range, many functions and high measurement accuracy.
The industrial pH meter is characterized by good stability, reliable operation, certain measurement accuracy, strong environmental adaptability, strong anti-interference ability, analog output, digital communication, upper and lower limit alarm and control functions.
The level of the acidity meter and the accuracy of the instrument are two different concepts, and the instrument level is not exactly the same as its accuracy. The level of the acidity meter is expressed by the index value (resolution or minimum display value) of its indicator (referred to as the electric meter). For example, an instrument with a division of 0.1 pH is called a 0.1-level instrument; the minimum display value is 0.001 pH. The instrument is called a 0.001 class instrument, and so on. The accuracy of the instrument is the comprehensive error of the standard solution of the electric meter and the electrode. It is not only related to the electric meter, but also related to the glass electrode and the reference electrode. Starting from the actual use requirements, the metering value of the electric meter is 0.1 to 0.001 pH. If necessary, according to the current state of the art, a more precise electric meter can be produced. However, due to structural and manufacturing reasons, the performance of commonly used electrodes has not been fully achieved.
The repeatability error of the glass electrode and the solution junction potential stability of the reference electrode were not better than 0.01 pH. Therefore, the resolution of the electric meter is higher, and the accuracy of the instrument test is hard to be better than 0.01 pH. However, choosing a high-resolution instrument can maximize or eliminate the impact of the meter on test errors. Since it is no problem to achieve satisfactory accuracy of the electric meter, it is constantly innovating and improving in terms of intelligence, humanization, reliability, ease of operation, and cost performance of the instrument. The relationship between the grade of the acidity meter and its test accuracy is specified in the National Metrology Verification Protocol (JJG119-84) of the acidity meter as follows:
PH acidity meter level 0.2, 0.1, 0.02, 0.01, 0.001
Grading value or minimum display value (pH) 0.2, 0.1, 0.02, 0.01, 0.001
Electric meter indication error (pH) ± 0.1, ± 0.05, ± 0.01, ± 0.01, ± 0.002
Total test error (pH) ± 0.2, ± 0.1, ± 0.02, ± 0.02, ± 0.01
Note: The test range for supporting test should be controlled within pH3~pH10. As can be seen from the above table, for a pH meter below 0.01, the total error value of the indication is equal to its level. For a pH meter of 0.01 grade, the total error of indication is 0.02 pH. For the 0.001 grade acidity meter, the total error of indication is It can only reach ±0.01pH, and it is necessary to use the primary pH standard material to be guaranteed. (Note: pH national standard materials are divided into primary and secondary. Generally, acidity meters are commonly used as secondary pH standards.)
With the development of scientific research and the advancement of production technology, quantitative analysis of water has been listed as one of the basic items of physical and chemical analysis of various substances, as an important quality indicator of various substances.
Different requirements for determining moisture are proposed based on the different moisture content of the different forms of the sample. Moisture determination can be the control analysis of industrial production, or the quality signing of industrial and agricultural products; the water content can be measured from tons of products.
The integrity of the electrodes should be checked first before proceeding. Calomel electrode . Since the composite electrode is widely used, the composite electrode is mainly discussed below.
The composite electrodes used in the laboratory are mainly closed-type and non-closed, and the closed-end type is relatively small, mainly based on the production of foreign enterprises. Before using the composite electrode, first check whether the glass bulb is cracked or broken. If not, use the pH buffer solution for two-point calibration. When the positioning and slope buttons can be adjusted to the corresponding pH value, it is generally considered that it can be used. Otherwise, it can be pressed. Use the instructions for electrode activation. The activation method is immersed in a 4% hydrogen fluoride solution for about 3 to 5 s, taken out and rinsed with distilled water, and then immersed in a 0.1 mol/L hydrochloric acid solution for several hours, rinsed with distilled water, and then calibrated, that is, pH value Position the 6.86 (25 ° C) buffer solution. After adjustment, select another pH buffer solution for slope adjustment. If it cannot be adjusted, replace the electrode. For the non-closed composite electrode, an external reference solution, ie 3 mol/L potassium chloride solution, is added, so it is necessary to check whether the potassium chloride solution in the electrode is more than 1/3. If not, add 3 mol/L. Potassium chloride solution. If the potassium chloride solution exceeds the pore location, the excess potassium chloride solution is removed, the solution is placed under the small hole, and the solution is checked for bubbles. If there is a bubble, the electrode should be lightly deflected to completely eject the bubble.
During use, the rubber on the electrode should be peeled off to expose the small hole. Otherwise, negative pressure will be generated during the analysis, which will cause the potassium chloride solution not to pass through the glass bulb and ion exchange with the solution to be tested. Will make the measurement data inaccurate. After the measurement is completed, the rubber should be restored and the small holes sealed. After the electrode is washed with distilled water, it should be immersed in 3 mol/L potassium chloride solution to keep the electrode bulb moist. If the protective solution has been lost before use, it should be soaked in 3 mol/L potassium chloride solution. A few hours to get the electrode to the best measurement state. In actual use, some analysts found that the composite electrode is treated as a glass electrode and is immersed in distilled water for a long time. This is not correct, which will greatly reduce the concentration of potassium chloride solution in the composite electrode, resulting in The electrode reaction is insensitive during the measurement, which ultimately leads to inaccurate measurement data, so the composite electrode should not be immersed in distilled water for a long time.
1. The glass electrode socket should be kept dry and clean. It is strictly forbidden to contact harmful gases such as acid mist and salt spray. It is strictly forbidden to touch the aqueous solution to ensure the high input impedance of the instrument.
2. When not measuring, short the input to avoid damage to the instrument.
3. New electrodes or electrodes that are not used for a long time must be soaked in distilled water for several hours before use. The electrode asymmetric potential is lowered to stabilize, and the internal resistance of the electrode is lowered.
4. When measuring, the electrode bulb should be fully immersed in the solution to be tested.
5, when used, should the inner reference electrode immersed in the solution and the internal reference, the internal reference solutions do not allow an end cap electrodes backward, so that floating internal reference.
6. When using, the rubber plug of the reference electrode electrolyte filling port should be removed, so that the reference electrolyte (salt bridge) can maintain a certain flow rate penetration by gravity and communicate with the measured solution. Otherwise, the reading will drift.
7. There should be no air bubbles in the potassium chloride solution to avoid disconnecting the measurement circuit.
8. Potassium chloride salt bridge solution should be added frequently to keep the liquid level higher than silver/silver chloride wire.
Must the pH measurement be calibrated?
pH measurement usually has two methods: colorimetric method (pH test paper or cuvette) and electrode method. Colorimetry, of course, should not be calibrated, and the electrode method must be calibrated, because the electrode method pH measurement is to compare the effect of the unknown solution with the standard solution of the known pHs in the measuring cell, which is the "operational definition of the electrode method pH measurement". "Determined.
The pH meter has many types depending on the design of the electric meter, and its operation steps are different. Therefore, the operation of the pH meter should be carried out in strict accordance with the instruction manual. In a specific operation, calibration is an important step in the operation of the pH meter. The data in Table 1 is the measured value of the pH meter with accuracy of 0.01 grade and passed the calibration test, and the calibration value can be seen from the calibration.
Although there are many types of pH meters, the calibration method uses a two-point calibration method, that is, two standard buffers are selected: one is pH7 standard buffer, and the second is pH9 standard buffer or pH4 standard buffer. First, the meter is positioned with pH 7 standard buffer, and then the second standard buffer is selected according to the acidity and alkalinity of the solution to be tested. If the solution to be tested is acidic, pH 4 standard buffer is used; if the solution to be tested is alkaline, pH 9 standard buffer is used. For manually adjusted pH meters, repeat the operation several times between the two standard buffers until the zero point and positioning (slope) knobs are adjusted, and the pH meter accurately displays the pH values ​​of the two standard buffers. The calibration process ends. Thereafter, the zero point and positioning knob should not be moved during the measurement. In the case of a smart pH meter, there is no need to repeat the adjustment because the pH of several standard buffers stored in the interior is available for selection and can be automatically identified and automatically calibrated. However, attention should be paid to the selection of standard buffers and the accuracy of their formulation. The intelligent 0.01 grade pH meter generally has three to five standard buffer pH values, such as the KL-016 pH meter from Kelilong.
Second, pay special attention to the temperature of the solution to be tested before calibration. In order to properly select the standard buffer, and adjust the temperature compensation knob on the meter panel to match the temperature of the solution to be tested. The pH of the standard buffer solution is different at different temperatures.
After the calibration is completed, the instrument does not need to be recalibrated within 48 hours for a frequently used pH meter. The instrument needs to be recalibrated if one of the following conditions is encountered:
(1) When there is a big difference between the solution temperature and the calibration temperature.
(2) The electrode is exposed to the air for too long, such as more than half an hour.
(3) The positioning or slope adjuster is mis-operated;
(4) after measuring a solution of peracid (pH < 2) or over-alkali (pH > 12);
(5) after changing the electrode;
(6) When the pH of the measured solution is not in the middle of the selected solution at the time of two-point calibration, and is further away from 7 pH.
1. The instrument should be calibrated according to the time period specified in the manual.
2. Pay attention to the calibration:
The standard buffer solution temperature is as close as possible to the temperature of the solution being tested.
The positioning standard buffer solution should be as close as possible to the pH of the solution being tested. Or two-point calibration, the pH of the solution to be tested should be as close as possible to the interval between the two standard buffer solutions.
After calibration, the electrode immersed in the standard buffer solution should be specially rinsed with water. Because of the buffering effect of the buffer solution, the measurement error is caused after being brought into the solution to be tested.
3. When recording the pH value of the solution to be tested, the temperature value of the solution to be tested should be recorded at the same time. Because of the temperature value, the pH value is almost meaningless. Although most pH meters have a temperature compensation function, they only compensate for the response of the electrodes, that is, only half compensation, and not simultaneously compensate the temperature of the solution to be tested, that is, full compensation.
How to avoid the reaction of the tested solution with the salt bridge components?
If the solution to be tested contains a soluble silver salt, a monovalent mercury salt or a cesium salt, the potassium chloride solution cannot be used in the salt bridge, and a satisfactory measurement result can be obtained by using a saturated potassium nitrate or ammonium nitrate solution. For the non-aqueous solution, a methanol solution of sodium iodide and an ethanol solution of potassium thiocyanate are used as an intermediate solution.
In short, it is impossible to cause precipitation and redox reaction of the components in the salt bridge solution and the solution to be tested, otherwise the electromotive force measurement may be disturbed.
For example, the application of a two-liquid reference electrode in measuring the concentration of Cl.
Common signal display instrument for pH meter ProtEX RT6820... Analog signal input type / integrated type display instrument input signal 4~20mA, Loop-Power loop supply voltage drop 2.8V, (5.8V with backlight) support Linear, square root or programmable math operation Loop-Power loop powered or DC powered backlight optional ProtEX RT6830.....pulse signal input type / integrated type display instrument battery powered, DC powered, or output loop powered battery Power supply, DC power supply, or output loop power supply backlight optional ProtEX_Lite PD663 Explosion-proof loop power supply process display instrument input signal 4~20mA voltage drop 1.7V, (4.9V with backlight) 3-1/2+LCDS digital, 0.6" high Loop-powered backlight with fast four-button programming problem
pH meters are widely used for pH testing of clean water, tap water, domestic water and various liquids. The pH is neutral at 7.0, acidic at 7.0 or lower, and alkaline at 7.0 or higher.
1. Storage of pH glass electrode
Short-term: stored in a buffer solution of pH=4;
Long-term: Stored in a buffer solution of pH=7.
2, pH glass electrode cleaning
Contamination of the glass electrode bulb may lengthen the electrode response time. The soil can be decontaminated with CCl 4 or soap, and then immersed in distilled water for a day and night to continue use. When the pollution is serious, immerse in 5% HF solution for 10-20 minutes, rinse immediately with water, then immerse in 0.1N HCl solution for a day and night and continue to use.
3, glass electrode aging treatment
The aging of the glass electrode is related to the gradual change of the rubber layer structure. The old electrode has a slow response, high membrane resistance, and low slope. Etching the outer layer with hydrofluoric acid often improves electrode performance. If this method is used to periodically remove the inner and outer layers, the life of the electrode is almost unlimited.
4. Storage of reference electrode
The best storage solution for the silver-silver chloride electrode is a saturated potassium chloride solution. The high concentration potassium chloride solution prevents the precipitation of silver chloride at the liquid junction and maintains the liquid junction in a working state. This method is also applicable to the storage of composite electrodes.
5. Regeneration of the reference electrode
Most of the problems with the reference electrode are caused by blockage of the liquid junction, which can be solved by the following methods:
(1) Soaking liquid junction: using a mixture of 10% saturated potassium chloride solution and 90% distilled water, heating to 60 to 70 ° C, immersing the electrode in about 5 cm, and soaking for 20 minutes to 1 hour. This method dissolves the crystals at the ends of the electrodes.
(2) Ammonia soaking: When the liquid junction is blocked by silver chloride, it can be diluted with concentrated ammonia. The specific method is to wash the electrode inside, and immerse the liquid in ammonia water for 10 to 20 minutes, but do not let ammonia water enter the inside of the electrode. The electrode was taken out and washed with distilled water, and the internal liquid was refilled and continued to be used.
(3) Vacuum method: The hose is placed around the reference electrode liquid junction, and the water suction pump is used, and the liquid in the suction part passes through the liquid junction to remove the mechanical blockage.
(4) Boiling solution junction: The liquid junction of the silver-silver chloride reference electrode is immersed in boiling water for 10 to 20 seconds. Note that the electrode should be cooled to room temperature before the next boil.
(5) When the above methods are invalid, the mechanical method of sandpaper grinding can be used to remove the blockage. This method may cause the sand under grinding to be inserted into the liquid junction. Causes permanent blockage.
The electrodes used in the laboratory are all composite electrodes, which have the advantages of being easy to use, not affected by oxidizing or reducing substances, and having a fast balancing speed. When in use, the rubber sleeve and the rubber sleeve at the lower end of the electrode filling port are completely removed to maintain the hydraulic pressure difference of the potassium chloride solution in the electrode. The following is a brief introduction to the use and maintenance of the electrode:
1. When the composite electrode is not used, it can be fully immersed in 3M potassium chloride solution. Do not dip with washing liquid or other water-absorbing reagents.
2. Check the bulb at the front end of the glass electrode before use. Under normal circumstances, the electrode should be transparent without cracks; the bulb should be filled with solution and no bubbles should exist.
3. When measuring a solution with a large concentration, shorten the measurement time as much as possible, and carefully clean it after use to prevent the test solution from adhering to the electrode and contaminating the electrode.
4. After cleaning the electrode, do not wipe the glass film with filter paper, and use filter paper to dry, avoid damage to the glass film, prevent cross-contamination, and affect measurement accuracy.
5. In the measurement, pay attention to the silver-silver chloride internal reference electrode of the electrode should be immersed in the chloride buffer solution in the bulb to avoid digital jumping phenomenon in the display part of the electricity meter. When using, be careful to gently rub the electrode a few times.
6. The electrode should not be used in strong acids, strong bases or other corrosive solutions.
7. It is strictly forbidden to use in dehydrating media such as absolute ethanol, potassium dichromate and the like.
1, pH glass electrode storage
Short-term: stored in a buffer solution with pH=4;
Long-term: Stored in a buffer solution of pH=7.
2, pH glass electrode cleaning
The pH meter is installed in both flow-through and immersion versions.
The sewage treatment plant generally chooses immersion installation. For example, the pH meter of the sewage treatment plant is installed in the outlet overflow tank of the grit chamber. The pH value here is representative and the water flow is stable, and the pH meter will not Caused a big impact. Regular maintenance helps to accurately measure the meter and extend the life of the meter. It should be noted that the dedicated cable between the sensor and the transmitter should not be wet, otherwise the high-impedance low-voltage signal of the electrode will not be transmitted to the transmitter.
If the electrode is not measured, the yellow protective sleeve should be put on, which can make the electrode wet, which is beneficial to prolong the service life of the electrode. Every other month or so, the electrode should be cleaned. Spray the attached material with a gentle water flow, then immerse the electrode in the cleaning solution for a while, then rinse with water.
The sensor bracket should also be cleaned. After each cleaning, the buffer solution is used for calibration. The manufacturer generally provides two standard solutions. One bottle has a pH equal to 7 and is used to calibrate the instrument zero point. One bottle has a pH equal to 4, which is used to calibrate the signal output slope of the meter. .
How to choose pH meter|acidity meter|acidity meter? There should be five major points to note.
When purchasing a pH meter, we must first consider the application, choose a pen pH meter, a portable acidity meter, a benchtop acidity meter or an industrial pH meter. Secondly, consider the accuracy required for the measurement and choose the accuracy that you can use yourself. BpH The -200A pH meter is widely used in industrial, electric power, agriculture, medicine, food, scientific research and environmental protection. The instrument is also an essential inspection equipment in the food factory, drinking water factory QS, HACCP certification.
We need to consider the following points when purchasing acidity timing:
1. According to the application classification, it can be divided into: pen pH meter, portable pH meter, laboratory pH meter and industrial pH meter. The pen type pH meter is mainly used to replace the function of the pH test paper, and has the characteristics of low precision and convenient use.
Portable pH meters are mainly used in field and field testing methods, requiring high precision and perfect functions.
The laboratory pH meter is a benchtop high-precision analytical instrument that requires high precision and full functionality, including printouts, data processing, and more.
Industrial pH meters are used for continuous measurement of industrial processes, not only have measurement display functions, but also alarm and control functions, as well as installation, cleaning, anti-interference and other issues.
2. According to the pH meter instrument accuracy classification: can be divided into 0.2, 0.1, 0.05, 0.01, the smaller the number, the higher the accuracy.
3. According to the component type classification: can be divided into transistor type, integrated circuit type and single-chip microcomputer type, more is the application of microcomputer chip, greatly reducing the instrument volume and stand-alone cost; but the development cost of the chip is very expensive
4 According to the reading indication classification: can be divided into two types: pointer type and digital display type. Pointer pH meters are rarely used, but pointer meters are capable of displaying continuous changes in data and are therefore used in titration analysis.
5. See if the pH meter has any additional functions, for example, with the standard RS232 interface, there is a very heavy temperature compensation is automatic
Still manual, the automatic temperature compensated pH meter is more convenient than the manual temperature compensated pH meter. You can understand the price between the two.
Remarks: pH meter|acidity meter|acidity meter, these three names have the same meaning, but different places or manufacturers say differently
1. What is the pH of water? What does it mean?
pH is one of the most important physical and chemical parameters of aqueous solutions. The natural phenomena involved in aqueous solutions, chemical changes, and production processes are all related to pH. Therefore, pH needs to be measured in industrial, agricultural, medical, environmental, and scientific fields.
The pH of the water is the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion activity in the water, expressed as:
pH= - lg aH +
The pH value is sometimes called the hydrogen ion index. Since the numerical value of the hydrogen ion activity is often small, it is inconvenient to use, so one of the pH values ​​is used as an indication of the acidity and alkalinity of the aqueous solution. Moreover, the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion activity can indicate the magnitude of the magnitude of the change in acidity and alkalinity, which is convenient to apply and thus obtains:
(1) Neutral aqueous solution, pH = - lg aH + = -lg10 -7 = 7
(2) acidic aqueous solution, pH<7, the smaller the pH value, the stronger the acidity;
(3) Alkaline aqueous solution, pH>7, the higher the pH value, the stronger the alkalinity.
pH measurement is a relative measurement that only indicates the difference in pH between the standard solution and the unknown solution. In actual measurement, calibration with a standard buffer solution is required. Therefore, in order to achieve consistent values, a pH scale must be established. The pH scale is set to 0 to 14 pH and the pH scale is determined by the pHs of the baseline buffer solution.
Therefore, the meaning of the pH scale can be expressed as: according to the pH definition, select several pH buffer solutions in the range of 0~14 pH as the fixed point of the pH scale, and determine their pHs using the most accurate method that can be achieved by contemporary techniques. value. There are two international pH scales, namely a variety of benchmark pH scales and a single benchmark pH scale. China uses a variety of benchmark pHs.
The pH buffer solution is a solution that keeps the pH stable. If a small amount of acid or base is added to the solution, or a small amount of acid or base is produced by a chemical reaction in the solution, and the solution is appropriately diluted, the pH of the solution is substantially constant, which is resistant to a small amount of acid. A solution which is alkali or diluted and which does not easily change the pH is called a pH buffer solution.
The pH standard buffer solution has the following characteristics:
(1) The pH of the standard solution is known and achieves the specified accuracy.
(2) The pH of the standard solution has good reproducibility and stability, and has a large buffer capacity, a small dilution value and a small temperature coefficient.
(3) The preparation method of the solution is simple.
How to prepare a pH buffer solution?
For general pH measurements, a complete pH buffering reagent (250 ml can be prepared) should be used. Deionized water should be used and boiled for 15 to 30 minutes to remove dissolved carbon dioxide. Cut the plastic bag and pour the reagent into the beaker, dissolve it with a proper amount of deionized water, rinse the bag, pour it into a 250ml volumetric flask, dilute to the mark, and shake well.
How to properly store and use pH buffer solution?
After the buffer solution is prepared, it should be packed in a glass bottle or a polyethylene bottle (alkaline pH buffer such as pH 9.18, pH 10.01, pH 12.46, etc., should be packed in a polyethylene bottle). Tight, stored in the refrigerator at low temperature (5-10 ° C), generally can be used for about two months, if found turbid, moldy or precipitated, etc., can not continue to use. When using, prepare a few 50ml polyethylene vials, pour the buffer solution in the large bottle into the vial, and let it stand for 1~2 hours at ambient temperature, and then use it after the temperature is balanced. After use, it should not be poured back into the large bottle to avoid contamination. The buffer solution in the vial can be used for 2~3 days under the environmental conditions of >10 °C. Generally, the pH of the solution can be used at pH 7.00, pH 6.86 and pH 4.00. Longer, the pH value of 9.18 and pH10.01 solution is easier to change due to the absorption of CO 2 in the air.
What is the use of pH buffer solution?
(1) Calibrate the pH meter before pH measurement.
(2) To verify the accuracy of the pH meter, for example, after calibrating the pH meter with pH 6.86 and pH 4.00, insert the pH electrode into the pH 9.18 solution, and check whether the displayed value of the instrument is consistent with the pH value of the standard solution.
(3) Check if the pH meter needs to be reset during general accuracy measurement. After the pH meter is calibrated and used, it may drift or change. Therefore, insert the electrode into the standard buffer close to the solution to be tested before the test, and determine whether it needs to be recalibrated according to the error.
(4) Detecting the performance of the pH electrode.
8. What are the advantages of using a bottled pH buffer solution?
It is also sold at pH meter distributors in pH standard buffers in polyethylene bottles. Compared with the buffer solution prepared by the pH buffering reagent itself, the buffer of different pH values ​​has different colors due to the addition of the color developing agent and the preservative, and it is not easy to be mistaken when used, and it is not stored at normal temperature. It is mildewed and has a shelf life of up to one year, so it is especially convenient to use. There are five kinds of pH 4.00, pH 6.86, pH 7.00, pH 9.18, pH 10.01, and there are two specifications of 500ml large bottle and 50ml small bottle.
What is the difference between a laboratory and an industrial pH electrode? In terms of use, the laboratory pH electrode is subjected to short-term intermittent test under good environmental conditions; and the industrial pH electrode is subjected to long-term continuous test under poor environmental conditions. In terms of performance, the laboratory pH electrode requires better accuracy and repeatability of the electrode, and the response is fast; while the industrial pH electrode requires good long-term stability of the electrode. Structurally, the pH electrode of the laboratory is simple and light, while the industrial pH electrode requires a firm structure, which can be installed and resists interference from various electric and magnetic fields.
Why should the pH electrode be soaked? How to properly soak? The pH electrode must be immersed before use because the pH bulb is a special glass membrane with a very thin layer of hydrated gel on the surface of the glass membrane that is only well wetted to respond well to H+ ions in solution. At the same time, the glass electrode is soaked, so that the asymmetric potential is greatly reduced and tends to be stable.
The pH glass electrode can generally be soaked in distilled water or a pH 4 buffer solution. It is generally preferred to use a pH 4 buffer, and the soaking time is 8 hours to 24 hours or longer, depending on the thickness of the bulb glass film and the degree of electrode aging. At the same time, the liquid junction of the reference electrode also needs to be immersed. Because if the liquid junction is dry, the liquid junction potential will increase or be unstable, the reference electrode soaking solution must be the same as the reference electrode's external reference solution, ie 3.3mol/L KCl solution or saturated KCl solution, the soaking time is generally It can be a few hours.
Therefore, for a pH composite electrode, it must be immersed in a pH 4 buffer containing KCl in order to simultaneously act on both the glass bulb and the liquid junction.这里è¦ç‰¹åˆ«æ醒注æ„ï¼Œå› ä¸ºè¿‡åŽ»äººä½¿ç”¨å•æ”¯çš„pH玻璃电æžå·²ä¹ 惯于用去离å水或pH4缓冲液浸泡,åŽæ¥ä½¿ç”¨pHå¤åˆç”µæžæ—¶ä¾ç„¶é‡‡ç”¨è¿™æ ·çš„浸泡方法引起的直接åŽæžœå°±æ˜¯ä½¿ä¸€æ”¯æ€§èƒ½è‰¯å¥½çš„pHå¤åˆç”µæžå˜æˆä¸€æ”¯å“应慢ã€ç²¾åº¦å·®çš„电æžï¼Œè€Œä¸”æµ¸æ³¡æ—¶é—´è¶Šé•¿æ€§èƒ½è¶Šå·®ï¼Œå› ä¸ºç»è¿‡é•¿æ—¶é—´çš„æµ¸æ³¡ï¼Œæ¶²æŽ¥ç•Œå†…éƒ¨ï¼ˆä¾‹å¦‚ç ‚èŠ¯å†…éƒ¨ï¼‰çš„KCl浓度已大大é™ä½Žäº†ï¼Œä½¿æ¶²æŽ¥ç•Œç”µåŠ¿å¢žå¤§å’Œä¸ç¨³å®šã€‚当然,åªè¦åœ¨æ£ç¡®çš„浸泡溶液ä¸é‡æ–°æµ¸æ³¡æ•°å°æ—¶ï¼Œç”µæžè¿˜æ˜¯ä¼šå¤åŽŸçš„。
å¦å¤–,pH电æžä¹Ÿä¸èƒ½æµ¸æ³¡åœ¨ä¸æ€§æˆ–碱性的缓冲溶液ä¸ï¼Œé•¿æœŸæµ¸æ³¡åœ¨æ¤ç±»æº¶æ¶²ä¸ä¼šä½¿pH玻璃膜å“应迟é’。æ£ç¡®çš„pH电æžæµ¸æ³¡æ¶²çš„é…制:å–pH4.00缓冲剂(250ml)一包,溶于250ml纯水ä¸ï¼Œå†åŠ å…¥56克分æžçº¯KClï¼Œé€‚å½“åŠ çƒï¼Œæ…拌至完全溶解å³æˆã€‚
pH电æžå¦‚何清洗?
çƒæ³¡å’Œæ¶²æŽ¥ç•Œæ±¡æŸ“åŽå…ˆç”¨ä»¥ä¸‹æº¶å‰‚清洗,å†ç”¨åŽ»ç¦»å水洗去溶剂,将电æžæµ¸å…¥æµ¸æ³¡æ¶²ä¸æ´»åŒ–。
污染物清洗剂
æ— æœºé‡‘å±žæ°§åŒ–ç‰©ä½ŽäºŽ1mol/L稀酸
有机油脂类物稀洗涤剂(弱酸性)
æ ‘è„‚é«˜åˆ†å物质稀酒精ã€ä¸™é…®ã€ä¹™é†š
蛋白质血çƒæ²‰æ·€ç‰©é…¸æ€§é…¶æº¶æ¶²ï¼ˆå¦‚食æ¯ç”Ÿç‰‡ï¼‰
颜料类物质稀漂白液ã€è¿‡æ°§åŒ–æ°¢
如何检测pH电æžçš„好å?用户å¯æŒ‰ä¸‹è¡¨æ•°æ®è‡ªè¡Œæ£€æµ‹pH电æžçš„好å,æ¥éª¤å¦‚
For instance, the seat should heat from 30-degrees C to 60-degrees C with three to five heating options. With such a unit, you can choose the perfect heating temperature that will suit every situation.


Heated Car Seat,Heated Seat Outdoor,Alloy Wire Heated Pads,Alloy Wire Car Heated Pads
JiLin Province Debang Auto Electric Co.,Ltd. , https://www.debangcarseatheating.com