Today's mobile phone batteries are all lithium batteries. Lithium is the smallest and most active metal on the chemical periodic table. It has a small volume and high capacity density. The chemical properties of lithium are too active. When exposed to air, lithium metal can explode with intense oxidation of oxygen. In order to improve safety and voltage, scientists have invented the use of graphite and lithium cobalt oxide (also lithium iron phosphate, lithium manganese oxide, ternary materials) and other materials to store lithium. 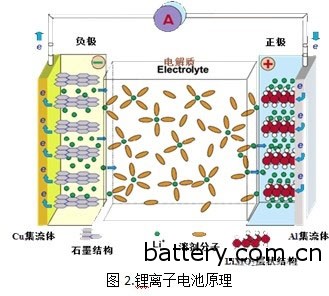
First, why is there a problem with the mobile phone battery?

The molecular structure of these materials forms a nanoscale fine storage grid that can be used to store lithium atoms. In this way, even if the battery casing is broken and oxygen enters, the oxygen molecules are too large to enter these fine cells, so that the lithium atoms do not come into contact with oxygen to avoid explosion.
When a lithium ion battery is charged , the lithium atom of the positive electrode loses electrons and becomes lithium ions. Lithium ions swim through the electrolyte (or polymer) to the negative electrode, enter the cell of the negative electrode, and obtain an electron, which is reduced to a lithium atom. When discharging, the entire program is reversed. A diaphragm with a number of fine holes is added to the battery to prevent short circuits. Good diaphragm paper can also automatically close the pores when the battery temperature is too high, so that lithium ions can not pass through, preventing danger.
However, in actual use, when an external short circuit occurs, the battery temperature will rise sharply to cause vaporization of the electrolyte, and the battery casing will rise and break, and lithium will encounter the oxygen in the air to ignite and burn. If there is no external short circuit, but the battery is not fine enough at the time of manufacture, there is a small impurity that pierces the diaphragm paper, causing an internal short circuit. When the problem is serious, a fire explosion may occur.
There is also a situation where it is overcharged. In the case of overcharging, the negative electrode will produce a lot of acicular lithium metal crystals, which will also pierce the diaphragm paper, causing an internal short circuit and thus causing a fire explosion.
In addition, high temperatures, impacts, and punctures can damage the diaphragm and even allow lithium to directly contact the oxygen in the air to explode.
It should be pointed out that in the case of an internal short circuit, the problem often occurs suddenly. You accidentally overcharged last night, and a short circuit occurred inside, but the heat of the battery slowly accumulated.
Wait until the next day at noon to put the phone in the pocket, the heat accumulated to a certain extent, the short circuit is more serious, will cause the phone to catch fire or explode, there is no warning before.
Second, how to prevent problems from appearing
Generally, the lithium battery we use has two kinds of lithium ion polymer and lithium ion battery. The former has no electrolyte. The problem is that it first expands, and the shell will ignite when it bursts. It will not suddenly explode. It has certain early warning and is relatively safe. . We try to buy this battery when we can choose.
For the user, it is best to use the mobile phone to charge directly (even if the battery is detachable) and charge with the original charger. Try to avoid using third-party chargers or universal chargers (for removable batteries).
In the case that the phone suddenly becomes extremely hot and the heat source is the battery, immediately move the phone away from the body to avoid bodily injury.
Lithium batteries have no way to guarantee 100% safety. All equipment that uses lithium batteries may explode and burn. What we can do is to minimize this probability.


Muck Truck,Mini Muck Truck,Muck Truck Wheelbarrow,Muck Car
Inner Mongolia Mengkai Import and Export Trading Co.,Ltd. , https://www.mkheavytruck.com