Injection Plastic Mesh Vegetable Crates with Lids
[ Instrumentation Network Instrument R & D ] Since the beginning of this year, the discovery of the medium and low temperature superconducting state of the heavy fermion material UTe2 has attracted a lot of attention. Nuclear magnetic resonance experiments found that its superconductivity may be a spin triplet pairing. Specific heat measurement revealed that its paired energy gap has a point node, but the specific heat coefficient is extended to half of the normal state at the zero temperature limit. Therefore, the theory suggests that the superconducting state is For non-positive iso-spin triplet pairing, only one spin orientation is paired, and the other spin orientation remains normal, which may have non-trivial topological excitation.

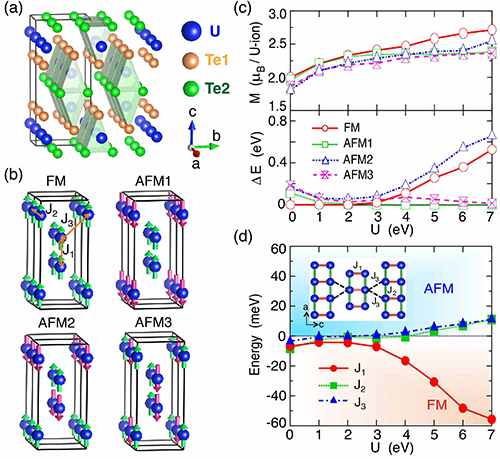
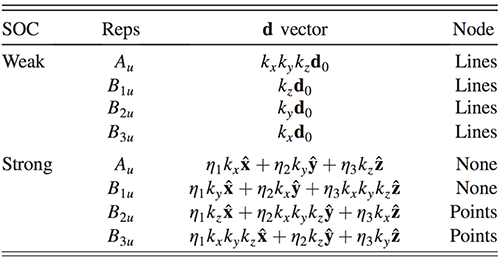
In order to understand the superconducting properties of UTe2, Yang Yifeng, a researcher in the EX9 team at the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences / Beijing National Research Center for Condensed Matter Physics, guided PhD students Xu Yuanhuan and Sheng Yutao to analyze the material carefully using the first-principles method (DFT + U) It is found that its magnetic and energy band properties are greatly affected by the f-electron coulomb effect. As shown in Figures 1 and 2, when the Coulomb effect is not taken into account, the band calculation gives the semiconductor band gap, which is inconsistent with the experiment. Only by introducing a strong Coulomb effect, the metal-type energy band required for the experiment can be obtained (Figure 1). The conclusion is also supported by the calculation of the dynamic mean field (DFT + DMFT). In this case, the magnetic properties of UTe2 exhibit a two-leg ladder structure (Figure 2), which is rare in the heavy Fermi system, and have two quasi-two-dimensional Fermi surfaces of the electron type and the hole type (Figure 3). . For such Fermi surfaces, symmetry analysis shows that only B2u or B3u representations with strong spin-orbit coupling have point nodes (Figure 4). Considering that the hole-type Fermi surface has a larger effective mass and better nesting, the superconducting state should be a B3u pair, and the point node is expected to be on the hole-type Fermi surface.
The above analysis means that the superconducting state of UTe2 in the zero field is not the non-positive spin pairings originally thought, and does not have the previously expected singular topological properties. At the same time, it is predicted that its extensional zero temperature specific thermal coefficient should approach zero. Interestingly, at the same time as the above work, new experiments found that the specific heat is upturned at a lower temperature, and the residual specific heat of the zero temperature epitaxy may be derived from some kind of quantum critical scattering contribution; thermal conductivity measurements also indicate that the carriers The concentration tends to zero at zero temperature, and the support point node is located in the a-axis direction (hole Fermi surface), which is consistent with the calculation. The special magnetic properties found in the theory mean that the system will exhibit complex behavior under the control of magnetic field and pressure, which is worthy of further study. PRL reviewers commented that this work provided a basic framework for understanding UTe2.
Relevant work was published in the Physical Review Letters [Phys. Rev. Lett. 123, 217002 (2019)] and received the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11774401, 11974397), the Ministry of Science and Technology (2017YFA0303103, 2015CB921303) and the Chinese Academy of Sciences Youth Promotion Committee, etc. support.

Custom Silicone Parts, Silicone Mold Machine Parts
Ningbo Jiongke Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.processingmfg.com